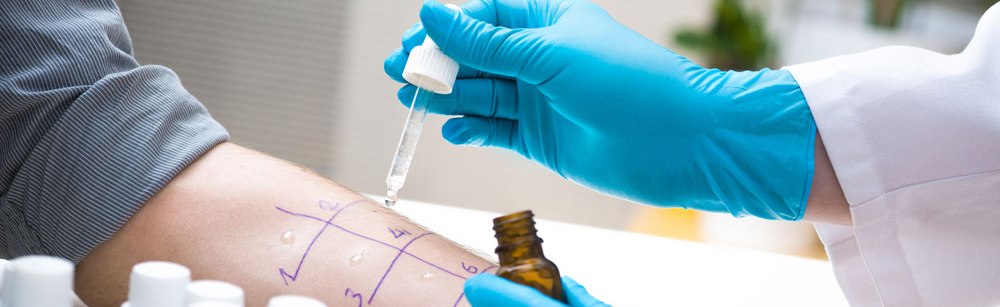
Diagnostics of Allergy
Allergy to various substances more often has the equal symptoms. Sometimes, it is very difficult to determine the cause of allergy without any special allergic tests. There are many methods of allergy diagnostics:
Skin Prick Testing
The traditional method of allergy diagnostics is the allergic tests. Make a scratch with a sterile scarifier and put a drop of diagnostic allergen. Evaluate results after 20 min. If there is swelling or erythema at the site of allergen application, test is positive. Evaluation of 15-20 tests is possible within one study. Pollen allergen tests are possible out of blooming season only (October-March).
Study of Specific IgE Antibodies
Increase in total level of IgE may be a sign of allergic diseases and other abnormal conditions. This method of study is used as screening test to confirm the allergic nature of disease.
For the diagnostics of “culprit allergen”, specific IgE are identified. These IgE are allergen-induced, and not produced as the clinical response (symptoms of allergic reaction). If blood serum of patient reacts with any allergen, it contains IgE-antibodies responsible for allergic reaction development.
Challenge Tests
Skin tests and blood study for IgE-antibodies identify allergens which potentially may induce the allergic reactions in the allergy person. If the diagnosis is unclear after skin tests and blood study, the doctor may prescribe the challenge tests. These tests are conducted in allergy in-patient care facilities, if medically strictly required. A small number of allergens are injected into the nose, under the tongue and directly into bronchi; reaction is evaluated after some intervals. This test may induce the severe allergic reaction in patient and shall be conducted in the presence of doctor who may render the immediate medical care.
Elimination Tests
If the contact with allergen is continuous, elimination tests are used to confirm that this specific allergen induces the clinical symptoms of allergy. Elimination is the allergen removal. The typical example of elimination test is elimination diet. This is the diagnostic method when the possible allergic product is fully excluded from the diet. If obvious improvement of disease will be on 7-14 days after product exclusion, it means that this product induces the allergy.
Allergy Treatment Methods
The principal and basic treatment of hypersensitivity is:
Elimination of Contact with Allergen
Elimination of contact with allergen is not only the treatment method, but also the allergy prevention. The less patient contacts with irritating substances, the lesser antibodies are produced. Therefore, the general inflammatory reaction reduces, symptoms of disease disappear gradually. To identify what substance induces the increased reaction of patient, the allergist conducts special allergic tests. It is practically impossible to determine the cause of allergy without these methods
Medicinal Treatment
Allergic reaction treatment methods include various groups of medicines to reduce the disease symptoms. These medicinal products have an effect on one of the secondary mechanisms of disease or its symptoms. These medicinal products are used during disease exacerbation only. However, after withdrawal of medicinal products from this group, symptoms of disease return very quickly.
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy holds a special place in the treatment of allergic diseases. This method implies the administration of “culprit” allergen extract to the patient with gradually increasing dose for a long period of time. It induces the correction of the immune response to this allergen.
In recent years, there has been a clear tendency to change the ASIT (allergen-specific immunotherapy) method towards more frequent use of sublingual therapy due to the injection therapy reduction. Tableted allergen administration methods have been tested and proposed. In many countries, doctors and patients have already appreciated the benefits of sublingual therapy, its high efficiency and ease of use.
It should be noted that the regional approach is correct in pollen allergy treatment. Allergens made of raw materials growing in one climatic-geographical region are less specific for the population of other regions. The differences in antigenic compositions of pollen and inflorescences of the same plants may result in diagnostic inaccuracies and, accordingly, negative treatment results. Even when the “culprit” allergen is diagnosed correctly, treatment with imported allergens may not have the fully expected positive effect, as in the treatment with regional (local) allergens.